Table of Contents
Setting up the Bullet world with a new robot
This tutorial will walk you though creating your own repo / metapackage from scratch that will use CRAM and Bullet world with your own robots. In this tutorial we will use the Hector Quadrotor robot as an example.
The starting point of this tutorial is an installation of CRAM including projection with PR2. If you followed the installation manual, you should have all the necessary packages already.
Robot URDF description
The first thing that we actually need is the robot, more precisely, its URDF description. For the quadrotor it is located in a repo on Github and if you're lucky it's also release as a Debian, so let's install it / clone it into our ROS workspace:
sudo apt-get install ros-YOUR-ROS-DISTRO-hector-quadrotor-description rospack profile # or cd ROS_WORKSPACE_FOR_LISP_CODE cd src git clone https://github.com/tu-darmstadt-ros-pkg/hector_quadrotor.git cd .. catkin_make
CRAM takes the URDF descriptions of the robots from the ROS parameter server, i.e., you will need to upload the URDFs of your robots as a ROS parameter. For our robot there is a launch file doing that, you will find it here:
roscd hector_quadrotor_description/launch/ && ls -l
It's called xacrodisplay_quadrotor_base.launch and has the following contents:
<launch> <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py $(find hector_quadrotor_description)/urdf/quadrotor.urdf.xacro" /> <param name="use_gui" value="True"/> <node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" ></node> <node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" /> <node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" /> </launch>
It includes a robot state publisher to publish the TF, we will need it to know the names of the TF frames of the robot later. It also starts Rviz:
roslaunch hector_quadrotor_description xacrodisplay_quadrotor_base.launch
(It also starts a GUI to play with the joint angles but let's ignore that.)
Let's check if the URDF's on the parameter server using RViz. For that, in RViz click:
Add -> RobotModel -> Robot Description: robot_description Add -> TF
To be able to see the TF frames choose base_link as the global fixed frame.
Directory / file setup
Now let's setup a directory structure for our own packages: a directory (repo) and the metapackage inside: in the src of a catkin workspace create a new directory, we will call it cram_quadrotor. Therein create a catkin metapackage with the same name:
mkdir cram_quadrotor && cd cram_quadrotor catkin_create_pkg cram_quadrotor && cd cram_quadrotor
Edit the CMakeLists.txt such that it contains only the metapackage boilerplate code:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3) project(cram_quadrotor) find_package(catkin REQUIRED) catkin_metapackage()
The first ROS package we will create will be the Prolog description of our robot. We will call it cram_quadrotor_description.
Go back to the root of your cram_quadrotor directory and create the package. The dependencies we will definitely need for now will be cram_prolog (as we're defining Prolog rules) and cram_robot_interfaces (which defines the names of predicates for describing robots in CRAM):
cd ..
catkin_create_pkg cram_quadrotor_knowledge cram_prolog cram_robot_interfaces
Now let's create the corresponding ASDF file called cram_quadrotor_knowledge/cram-quadrotor-knowledge.asd:
;;; You might want to add a license header first (defsystem cram-quadrotor-knowledge :author "Your Name" :license "BSD" :depends-on (cram-prolog cram-robot-interfaces) :components ((:module "src" :components ((:file "package") (:file "quadrotor-knowledge" :depends-on ("package"))))))
Now create the corresponding src directory and a cram_quadrotor_knowledge/src/package.lisp file in it:
;;; license (in-package :cl-user) (defpackage cram-quadrotor-knowledge (:use #:common-lisp #:cram-prolog #:cram-robot-interfaces))
Also, an empty cram_quadrotor/cram_quadrotor_knowledge/src/quadrotor-knowledge.lisp.
Now, let's compile our new packages (catkin_make) and load them through the REPL (you need to restart your REPL after you create a new ROS package so that it finds it):
CL-USER> , ros-load-system cram_quadrotor_knowledge cram-quadrotor-knowledge
Boxy Prolog description
Now, let's describe our robot in Prolog, such that we could do some reasoning with it.
We fill in the file cram_quadrotor/cram_quadrotor_knowledge/src/quadrotor-knowledge.lisp with some simple descriptions of our robot, which are the ones relevant for navigation and vision. For robots with arms one could also implement manipulation-specific functionality but this is too complex for the scope of this tutorial.
As can be seen from the TF tree, our robot has 3 camera frames, 1 depth and 1 RGB frame from a Kinect camera, and an RGB frame from a Kinect2 camera.
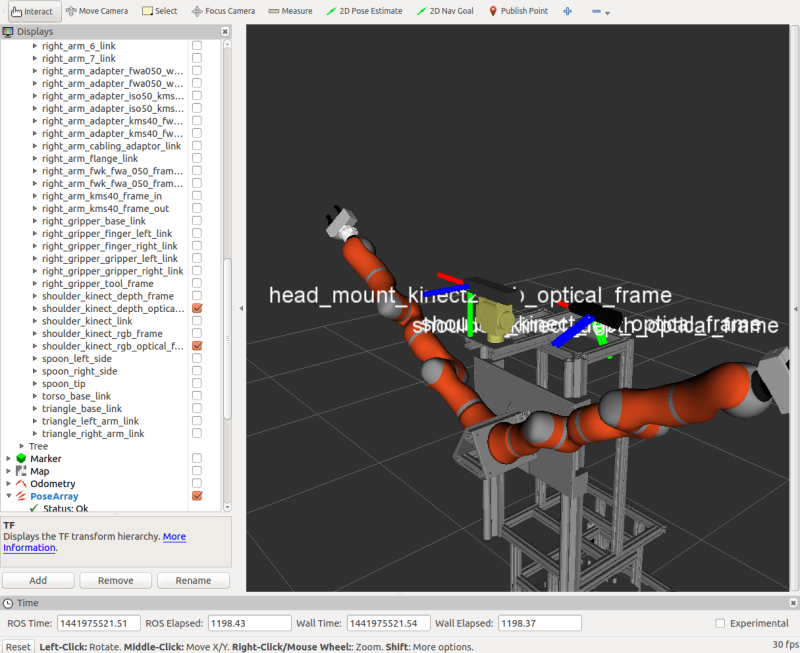
It's camera can be from 1.60 m to 2.10 m above the ground, depending on the torso position. It also has a pan-tilt-unit.
;;; license
(in-package :cram-boxy-knowledge)
(def-fact-group boxy-metadata (robot
camera-frame
camera-minimal-height camera-maximal-height
robot-pan-tilt-links robot-pan-tilt-joints)
(<- (robot boxy))
(<- (camera-frame boxy "head_mount_kinect2_rgb_optical_frame"))
(<- (camera-frame boxy "shoulder_kinect_rgb_optical_frame"))
(<- (camera-frame boxy "shoulder_kinect_depth_optical_frame"))
(<- (camera-minimal-height boxy 1.60))
(<- (camera-maximal-height boxy 2.10))
(<- (robot-pan-tilt-links boxy "pw070_box" "pw070_plate"))
(<- (robot-pan-tilt-joints boxy "head_pan_joint" "head_tilt_joint")))
Finally, compile the file (Ctrl-c Ctrl-k).
Loading the world
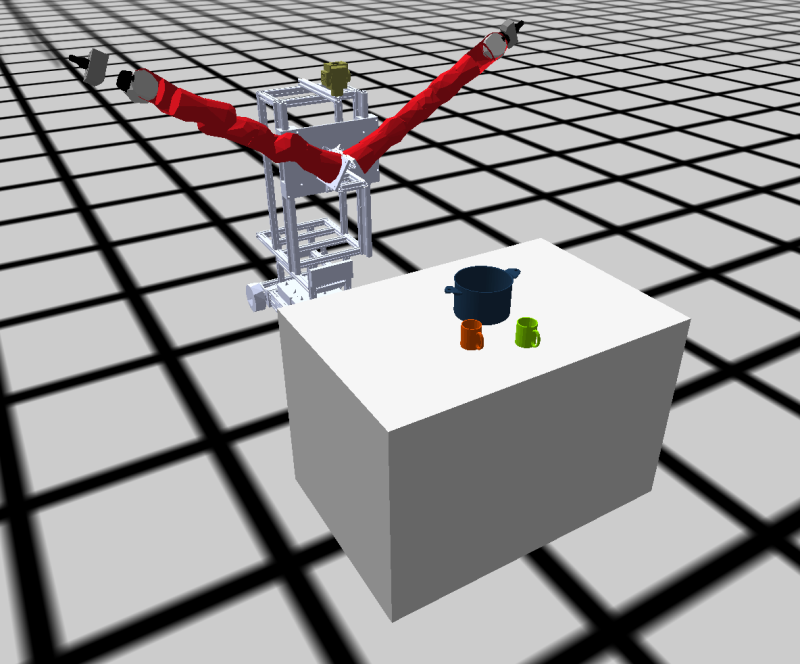
Now let's try to load our robot also into the Bullet world. We will spawn the floor, the robot, and a couple of household objects.
For that, we
- load the bullet reasoning package in the REPL
- start a ROS node
- spawn the robot and the floor
- spawn a big box for a table and a couple of household objects to go on top
;; step 1 (asdf:load-system :cram-bullet-reasoning) (in-package :btr) ;; step 2 (roslisp:start-ros-node "cram_bullet_boxy") ;; step 3 (let ((robot-urdf (cl-urdf:parse-urdf (roslisp:get-param "robot_description")))) (prolog `(and (clear-bullet-world) (bullet-world ?w) (debug-window ?w) (robot ?robot) (assert (object ?w :static-plane floor ((0 0 0) (0 0 0 1)) :normal (0 0 1) :constant 0 :disable-collisions-with (?robot))) (assert (object ?w :urdf ?robot ((0 0 0) (0 0 0 1)) :urdf ,robot-urdf))))) ;; step 4 (prolog `(and (bullet-world ?w) (assert (object ?w :box table-0 ((2.1 0 0.5) (0 0 0 1)) :size (0.7 1.5 1) :mass 10.0)) (assert (object ?w :mesh pot-0 ((2 0 1.1) (0 0 0 1)) :mass 0.5 :color (0.1 0.2 0.3) :mesh :pot)) (assert (object ?w :mesh mug-0 ((2.2 -0.2 1.07) (0 0 0 1)) :mass 0.2 :color (0.8 0.3 0) :mesh :mug)) (assert (object ?w :mesh mug-1 ((2.3 0 1.07) (0 0 0 1)) :mass 0.2 :color (0.5 0.8 0) :mesh :mug))))
Reasoning with Boxy
Let's try some reasoning:
BTR> (prolog '(visible ?world ?robot pot-0)) NIL
The query asks if the object pot-0 is visible to the robot.
The answer is “No”, as our robot is very tall and look straight ahead.
Now let's put the object higher and try again:
BTR> (prolog '(and (bullet-world ?w) (assert (object-pose ?w pot-0 ((2 0 2) (0 0 0 1)))))) BTR> (prolog '(visible ?world ?robot pot-0)) (((?WORLD . #<BT-REASONING-WORLD {100D78C5F3}>) (?ROBOT . CRAM-BOXY-KNOWLEDGE::BOXY)) . #S(CRAM-UTILITIES::LAZY-CONS-ELEM :GENERATOR #<CLOSURE # {101275A8FB}>))
Now it is visible.
Let's put the pot down:
BTR> (simulate *current-bullet-world* 50)
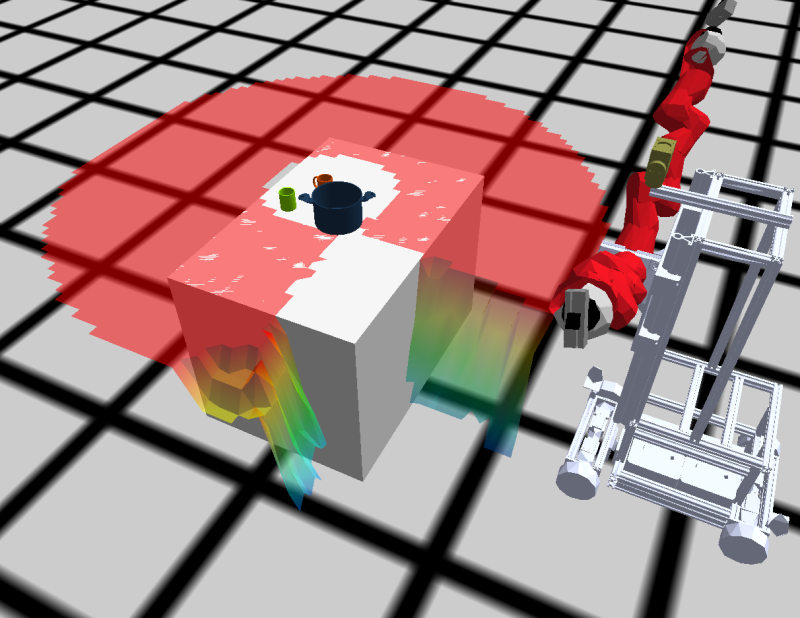
Now let's do something more complex: let's generate a visibility costmap, that will generate poses from where Boxy will be able to see the pot. As we're going to be using costmaps, we will need to define costmap metadata first:
BTR> (def-fact-group costmap-metadata () (<- (location-costmap:costmap-size 12 12)) (<- (location-costmap:costmap-origin -6 -6)) (<- (location-costmap:costmap-resolution 0.05)) (<- (location-costmap:costmap-padding 0.35)) (<- (location-costmap:costmap-manipulation-padding 0.35)) (<- (location-costmap:costmap-in-reach-distance 1.0)) (<- (location-costmap:costmap-reach-minimal-distance 0.1)))
We should also load the cram_bullet_reasoning_designators package, as visibility costmap is implemented in it:
BTR> (asdf:load-system :cram-bullet-reasoning-designators)
Now let's create a location designator for a pose to see the mug-0 object, which is the orange mug in the corner, and try to resolve it:
BTR> (let ((location-to-see (desig:make-designator :location '((:to :see) (:object mug-0))))) (desig:reference location-to-see))